From their niche in boutique residential, matte black and brushed gold bathroom faucet finishes have moved squarely into mainstream commercial and institutional construction. Architects and engineers who specify Division 22 plumbing systems consider these finishes now regularly through the lenses of durability, accessibility, sustainability, and system integration. This 2025 technical review outlines the engineering-grade considerations for specification in airports, higher education, healthcare, corporate offices, and civic facilities.
1. Design Drivers in 2025: Architectural and Material Trends
As a result, design teams have moved toward darker, low-gloss, warm metallic finishes that support contemporary restroom palettes. A greater use of engineered stone, terrazzo, matte porcelain tiles, and composite counters has driven the need for finishes that provide contrast without reflective glare.
Context regarding architectural trend and materials can be referenced through the American Institute of Architects, AIA, material resources at:
From a technical standpoint, finish selection must take into account long-term performance in high-use facilities. The longevity of the finish is not an aesthetic preference; it is a building lifecycle requirement.
2. Technology and Engineering Performance Complete
PVD and Advanced Coatings
Most of the commercial matte black and brushed gold faucets are coated with PVD due to its excellent adhesion and chemical resistance. PVD coatings minimize micro-pitting, resist cleaners containing chlorides, and do not discolor under UV lighting.
Engineers shall consider manufacturer PVD specifications in concert with referenced standards. ASME provides minimum performance requirements for plumbing fittings under ASME A112.18.1/CSA B125.1 that can be purchased at:
ASME plumbing supply fittings standard
Color is not specified in the ASME code, but endurance and corrosion tests establish a base of mechanical integrity for which the finish system must persist.
Powder Coatings and Organic Finishes
Some matte finishes use architectural powder coats or organic coatings. These should be tested for compatibility with cleaning chemicals. The Society for Protective Coatings, SSPC has technical guidance on coating durability at:
SSPC coating durability resources
PVD generally outperforms organic coatings for institutional environments that have aggressive disinfection protocols.
3. Accessibility and ADA Considerations
ADA implications extend beyond fixture placement. Finish reflectivity and contrast can have an impact on usability by people with low vision. The 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design have lavatory and faucet accessibility requirements which address control operability and reach ranges, available at:
2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design
Additional technical guidance on lavatory controls can be obtained from the U.S. Access Board at:
U.S. Access Board ADA Chapter 6: Lavatories and Sinks
Key ADA implications of matte black and brushed gold include:
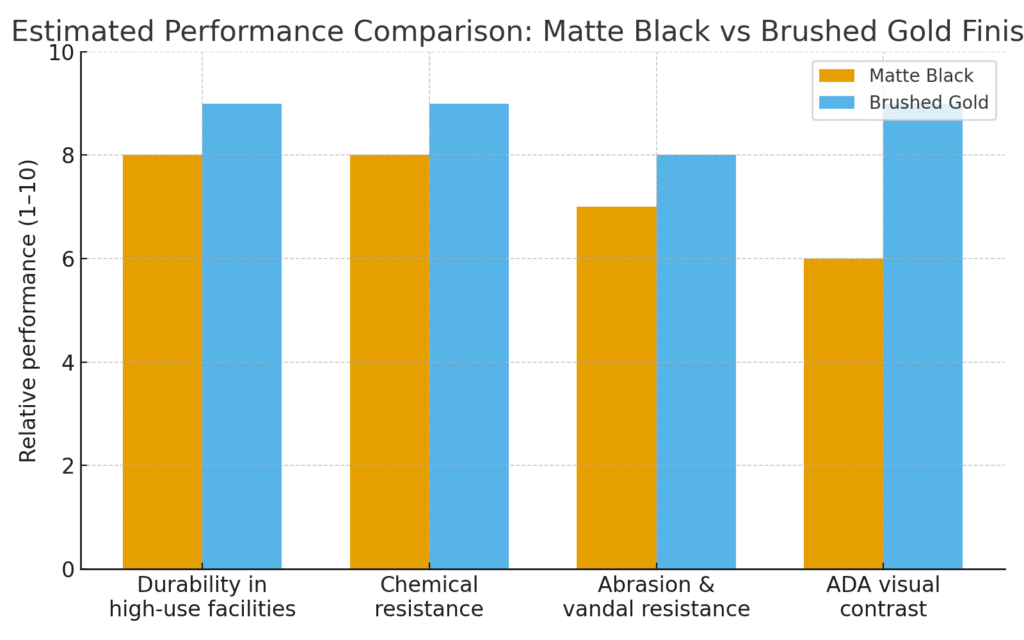
Visual Contrast: Matte black may blend into dark counters, reducing detectability. Brushed gold often provides better visual recognition.
Control Operability: This is the ability, per ADA section 606.4, to operate with one hand, without tight grasping or rotation, and with ≤5 lbf of force.
Surface Temperature: The dark finishes in sunlight can get quite hot, and thermal safety may need to be considered for glass-heavy atriums or airports.
4. Water Efficiency Requirements: WaterSense and CALGreen
EPA WaterSense Compliance
WaterSense-labeled faucets meet a maximum of 1.5 gpm at 60 psi while meeting performance criteria. EPA resources for faucet efficiency are available at:
See EPA WaterSense bathroom faucets
For general WaterSense program information, visit:
When specifying alternative finishes, the teams must verify that the exact finish-specific model number retains WaterSense certification. Not every finish automatically inherits the listing.
CALGreen Requirements
In California or CALGreen-influenced jurisdictions, indoor water use reduction targets 20-25% affect the selection of fixtures. The California Green Building Standards Code is available at:
California Green Building Standards Code (CALGreen)
Technical chapters on nonresidential plumbing requirements are available from ICC at:
ICC CALGreen 2022, Chapter 5 – Nonresidential Mandatory Measures
Completion selection has no effect on sustainability documentation unless flow-regulating components vary across different models or series.
5. Cleaning, Chemical Resistance, and Infection Control
Harsh disinfectants include quaternary ammonium compounds, chlorine solutions, and alcohol-based cleaners. Facilities such as hospitals, laboratories, schools, and transit centers use these frequently. The finish must be able to resist repeated chemical exposure without softening, clouding or discoloring.
For infection control references, the CDC’s environmental cleaning guidance can be found at:
CDC environmental infection control guidance
Matte black coatings, especially organic types, can streak or produce sheen spots when wiped aggressively. Brushed gold PVD is usually more uniform over time. Design teams should specify:
Cleaning compatibility charts
Chemical-resistance test, accelerated
Mock-up demonstrations for critical environments
6. Abrasion and Vandal Resistance in High-Traffic Settings
Public buildings expose faucet finishes to abrasion from rings, keys, bags, and routine scrubbing. Guidance on abrasion testing is supported in standards including ASTM D4060 (Taber abrasion), available from ASTM International:
ASTM D4060 Taber abrasion standard
Darker finishes have bright scratches when the substrate is exposed. In high-risk environments—transportation terminals, student centers, detention facilities—the following should be done by the design teams:
Specify minimum abrasion thresholds
Use PVD over solid brass or stainless steel
Avoid soft organic coatings on dark finishes
Standardize finishes across campuses to ensure consistency in replacement
7. Integration with Sensors, Mixers, and Building Systems
Sensor Performance with Dark Finishes
Infrared sensors may behave differently on dark, low-reflectance surfaces. Sensor windows must be optically stable and protected against micro-scratching caused by cleaning.
Considerations for integration engineering include the following :
Detection range calibration
Durability of window materials
Hard-wired versus battery power design
Maintenance access shall not damage the finish.
Guidance on the commissioning of sensor faucets and energy considerations can be aligned with ASHRAE design practices:
BMS Integration and Central Mixing Valves
Large institutional projects increasingly incorporate faucets featuring: Central tempering systems Digital mixing valves Hot-water recirculation monitoring BMS alarming for outages or temperature variance Finish selection affects lifecycle planning, especially when decorative fixtures must remain visually consistent while their electronics are upgraded.
8. Specification Recommendations for Division 22 Documentation
The architectural and MEP teams shall consider the following technical requirements:
Separate Finish Requirements from Mechanical Performance
Base mechanical and hydraulic performance shall refer to ASME A112.18.1/ CSA B125.1. Finish requirements shall specify PVD or equivalent processes that are independently verified for corrosion and abrasion resistance.
Require finish-specific compliance documentation
Submittals must confirm that the finish variant carries the same approvals as the base model. Sometimes manufacturers certify only chrome models.
Address ADA Visual Contrast and Operability
Whenever dark counters are used, pairing them with matte black should consider low-vision accessibility. Brushed gold often offers greater detectability.
Include Clear Maintenance Instructions
O&M documentation should include specific cleaning methods consistent with facility protocols.
Conclusion
By 2025, matte black and brushed gold faucet finishes have matured into viable, durable options for demanding commercial and institutional projects. When evaluated through the lens of ASME mechanical requirements, ADA accessibility, EPA WaterSense guidelines, CALGreen water-efficiency mandates, and real-world maintenance demands, these finishes can align with both performance and architectural objectives. Finish selection is more than a design decision; it is a system-level specification choice that affects durability, accessibility, operations, and lifecycle management. To the architect and engineer, matte black and brushed gold are representative not of temporary aesthetic trends but of long-term, technically defensible finish strategies for the contemporary built environment.
| Topic | Standard / Resource | Link (title only) |
|---|---|---|
| Architectural material trends | American Institute of Architects (AIA) material resources | AIA material resources |
| Plumbing mechanical performance | ASME A112.18.1 / CSA B125.1 | ASME plumbing supply fittings standard |
| Coating durability | Society for Protective Coatings (SSPC) guidance | SSPC coating durability resources |
| ADA lavatories & faucets | 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design | 2010 ADA Standards for Accessible Design |
| ADA lavatory control guidance | U.S. Access Board – ADA Chapter 6 | U.S. Access Board ADA Chapter 6: Lavatories and Sinks |
| Water efficiency – faucets | EPA WaterSense – bathroom faucets | EPA WaterSense bathroom faucets |
| Water efficiency – general program | EPA WaterSense program | EPA WaterSense program |
| California water-efficiency code | CALGreen – California Green Building Standards Code | California Green Building Standards Code (CALGreen) |
| Nonresidential plumbing measures | ICC CALGreen 2022, Chapter 5 | ICC CALGreen 2022 Chapter 5 – Nonresidential Mandatory Measures |
| Infection control & cleaning | CDC environmental infection control guidance | CDC environmental infection control guidance |
| Abrasion testing | ASTM D4060 (Taber abrasion) | ASTM D4060 Taber abrasion standard |
| Sensor commissioning / energy use | ASHRAE design practices | ASHRAE resources |
No responses yet