Specifying Faucets for Healthcare Environments: Standards, Materials, and Compliance
Health care faucets must balance infection control, accessibility, water efficiency, and durability.
This guide outlines specification criteria aligned with ADA, EPA WaterSense, CALGreen, and ASME standards—covering materials, hydraulics, and system integration.
This page was reviewed on February 7, 2026 to reflect current healthcare sink-and-faucet specification practices, including accessible control requirements,
low-flow performance constraints, infection-control geometry considerations (splash/aerosol minimization), and how WaterSense/CALGreen flow limits interact
with clinical handwashing needs. The content below is structured to support AEC teams with documentation-ready references and repeatable checklist criteria.
Regulatory and Standards Framework
ADA Requirements for Accessible Lavatory Faucets
Key ADA references for healthcare plumbing fixture compliance:
Key requirements related to faucets include:
- Operable with one hand without tight grasping, pinching, or twisting of the wrist.
- Maximum operating force: 5 lbf (22.2 N).
- Controls within ADA reach ranges.
- Under-sink piping insulated or arranged to avoid contact.
Specification Implications
- Use lever handles, wrist-blade handles, or sensor-operated faucets.
- Coordinate heights and clearances of lavatories with ADA requirements.
- Insulate or enclose supply and drain piping.
Water Efficiency: EPA WaterSense
WaterSense specifies efficiency and performance criteria for lavatory faucets.
Typical WaterSense criteria:
- 1.5 gpm maximum at 60 psi (historical requirement)
- 0.8 gpm minimum at 20 psi
- Draft revisions reduce maximum to 1.2 gpm
Healthcare Implications
- WaterSense faucets are common in public/visitor and staff restrooms.
- Clinical handwash stations may require higher flow for rinsing and splash control.
- Specify WaterSense only where clinically appropriate and code-compliant.
CALGreen and Jurisdictional Requirements
CALGreen sets mandatory nonresidential flow-rate limits.
Common CALGreen provisions:
- 0.5 gpm maximum at 60 psi
- Metering faucets: ≤ 0.20 gallons per cycle
Specification Implications
- Where CALGreen applies, its stricter limit typically governs public lavatory fixtures.
- Coordinate clinical flow targets with function + local code adoption.
ASME A112.18.1/CSA B125.1 — Plumbing Supply Fittings
This standard defines design, performance, and endurance requirements for faucets.
Includes:
- Flow rate tolerances
- Endurance cycle testing
- Corrosion resistance testing
- Pressure/temperature testing
Specification Implications
- Healthcare faucets should be listed to ASME A112.18.1/CSA B125.1 (or equivalent recognized listing).
- WaterSense labeling layers on top of the base ASME/CSA performance listing.
Infection-Control Considerations
Sink and Faucet as Pathogen Vectors
Healthcare sinks are recognized reservoirs. Design should reduce splash, aerosolization, and biofilm risk.
Key considerations:
- Use deeper basins with appropriate spout offset to reduce splash.
- Avoid directing flow toward the drain.
- Prefer smooth surfaces with minimal ledges.
Spout Reach, Height, and Offset
- Hand-washing stations typically require adequate spout reach for full-hand clearance.
- Offset spout outlet away from the drain to reduce splash/aerosolization risk.
- Hands-free control is often preferred in clinical zones to reduce contact points.
Video Reference
Practical Design Checklist
For each faucet, verify:
- Intended use zone (public, staff, clinical, scrub)
- ADA compliance: reach, controls, barriers
- Infection-control review of spout and basin geometry
- WaterSense/CALGreen compliance where applicable
- ASME listing and flow compatibility with TMVs
- Sensor/BAS integration needs
- Maintainability and spare-parts standardization
Summary Table
| Dimension | Key Criteria / Targets | Main References |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility (ADA) | One-hand operation; no tight grasping/pinching/twisting; ≤ 5 lbf operating force; controls within reach; under-sink piping insulated/guarded. | ADA 2010 + Access Board Chapter 6 |
| Water Efficiency | WaterSense: 1.5 gpm max @ 60 psi (draft 1.2), 0.8 gpm min @ 20 psi; CALGreen: 0.5 gpm max @ 60 psi; metering ≤ 0.20 gal/cycle. | WaterSense + CALGreen |
| Listings & Performance | Faucets listed to ASME A112.18.1/CSA B125.1 (flow tolerance, endurance, corrosion, pressure/temperature tests). | ASME A112.18.1 |
| Infection Control | Deep basins, offset spouts, laminar flow in clinical zones; avoid directing flow at drain; smooth cleanable surfaces; hands-free preferred. | CDC + Alberta + FGI |
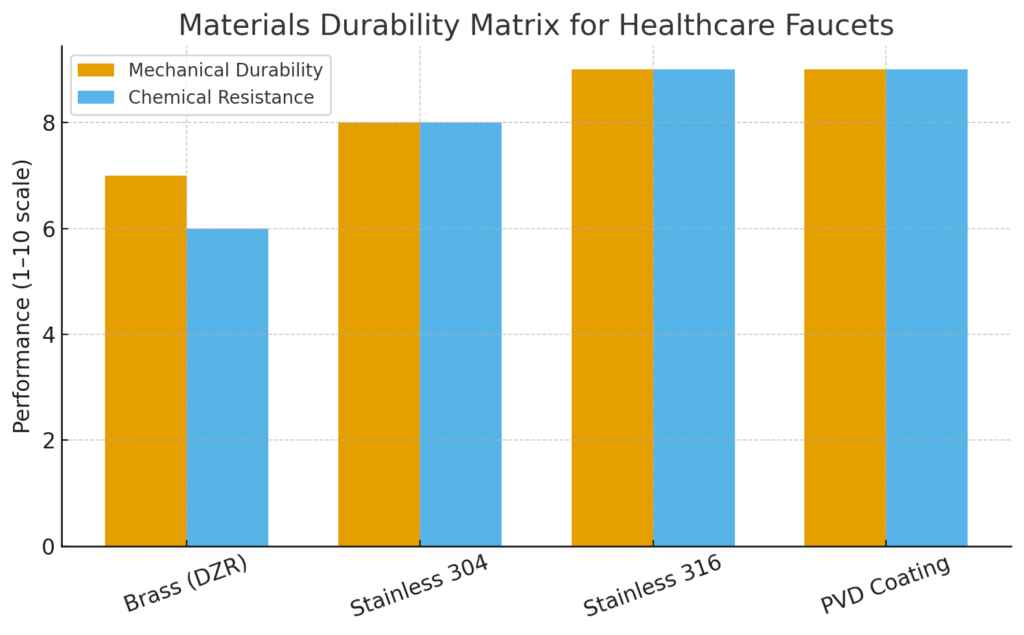
| Materials & Finishes | Low-lead DZR brass or 304/316 stainless; corrosion-resistant internals; PVD finishes; smooth, non-textured surfaces. | ASME tests + manufacturer data |
| Thermal Safety & TMVs | TMVs typically ≤ 110°F (43°C); must operate at low flows; supports Legionella water-management strategy. | CDC Water Management |
| Lifecycle & Maintenance | Serviceability focus: top-access components where possible; accessible checks/screens; cartridge standardization; spare-parts planning. | O&M standards |